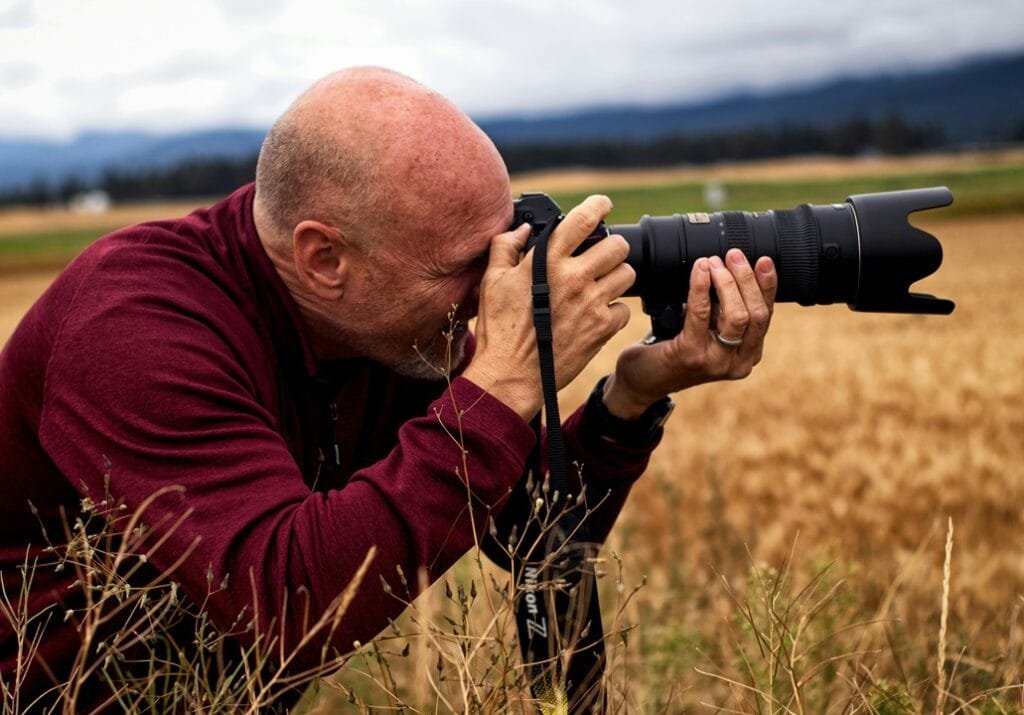
If you are interested to know about Telephoto Photography then here is The Ultimate Comprehensive Guide to capturing Stunning Distant Shots with Precision and Creativity.
Telephoto photography is one of the most captivating and powerful styles of photography. It enables photographers to capture subjects that are far away, bringing them closer to the viewer in a way that’s both dramatic and beautiful. By using lenses with long focal lengths, telephoto photography allows you to magnify distant scenes or objects while still maintaining incredible detail and sharpness. Whether you’re interested in wildlife, landscapes, or even portraits, telephoto lenses can transform your photography in remarkable ways.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of telephoto photography, from understanding how telephoto lenses work to how they can help you capture the perfect shot. Let’s dive in.
What is Telephoto Photography?
At its core, telephoto photography is about magnifying subjects that are far away using specialized lenses with long focal lengths. These lenses allow photographers to shoot objects, animals, or scenes that would otherwise be inaccessible or too distant for a standard lens. Telephoto lenses are often seen in action during wildlife, sports, and nature photography, but they can be used for a variety of purposes.

Both images taken from exact same point of view & same full frame camera. Left 50mm focal length & Right: 24mm focal length.
Common misconception about telephoto photography is that it’s only about zooming in. While zooming is an important feature, telephoto lenses are also known for compression—a unique effect where objects in the background appear closer to the subject. This creates an illusion of depth, making the image feel more intense and immersive.
The Unique Benefits of Telephoto Lenses
Compression Effect-Telephoto Photography: The Ultimate Guide
One of the most distinctive benefits of telephoto lenses is the compression effect. This phenomenon makes elements in the background seem closer to your subject, which is especially helpful when you want to emphasize the size or importance of certain features in the frame. For instance, if you’re photographing a person standing in front of a vast mountain range, the telephoto lens can make the mountains appear much closer, creating a visually striking image.
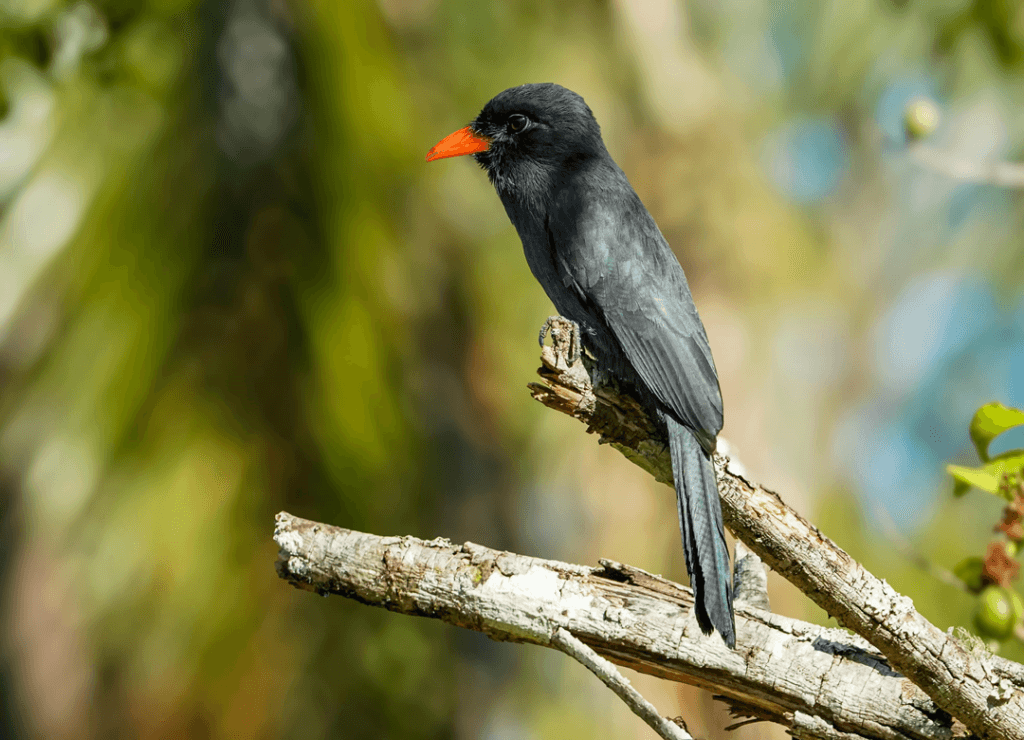

Bringing Distant Subjects Into Focus-Telephoto Photography: The Ultimate Guide
Telephoto lenses are perfect for subjects that are physically far away but need to be captured in detail. Wildlife photographers, for example, often rely on telephoto lenses to capture close-up images of animals without disturbing them. Imagine trying to photograph a lion or a rare bird—you’d need the magnification power of a long lens to get those intimate shots without disturbing the animal’s natural behavior.
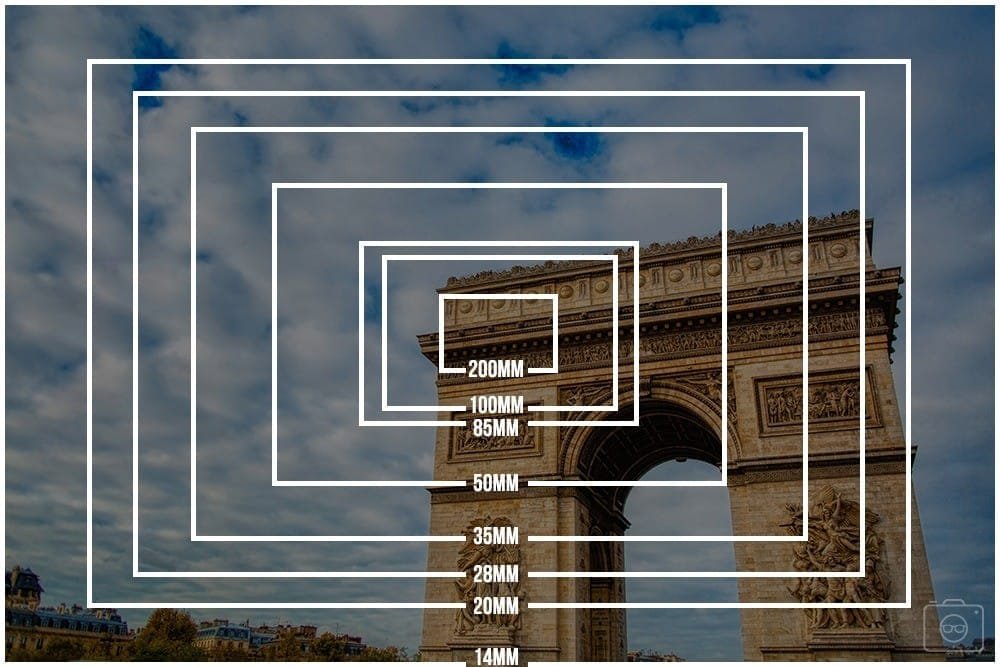
Highlighting Scale and Size-Telephoto Photography: The Ultimate Guide
Telephoto lenses excel at showing scale in photography. According to professional photographers, describes telephoto photography as a tool that allows you to “show scale” by emphasizing the size differences between objects. For example, placing a small human figure in front of a massive mountain can make the person appear tiny and insignificant, whereas a wide-angle lens might make everything seem the same size. The dramatic effect is achieved through the lens’s long focal length and its ability to flatten the perspective.
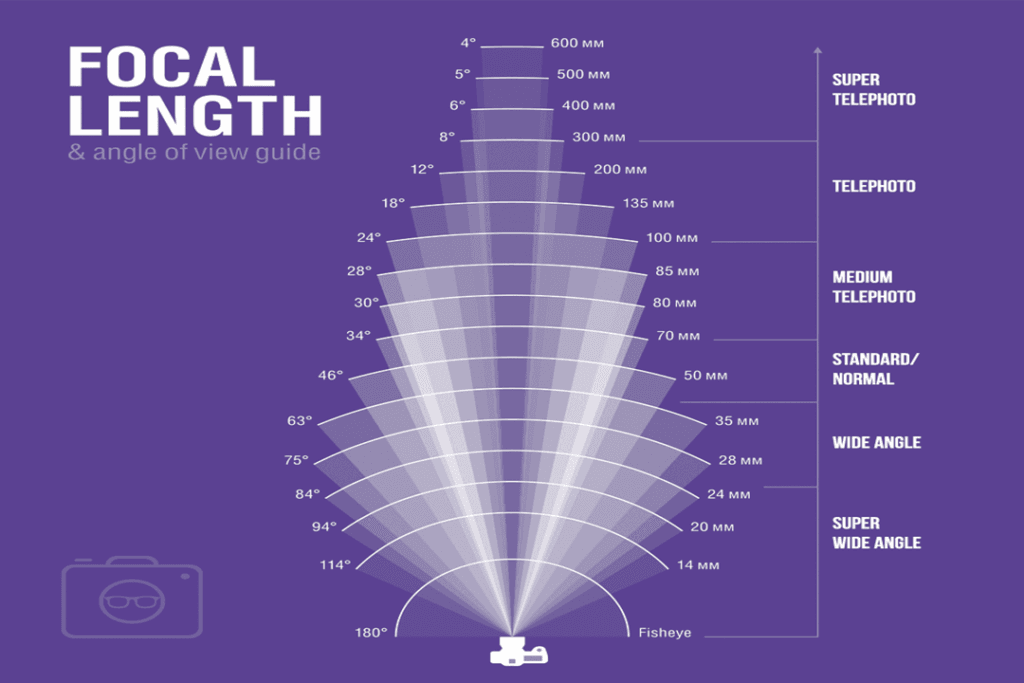
You can see based on the chart that the longer the focal length of your lens, the narrower the angle of view. And it’s logical right, the more you zoom in, the less you’re able to see on the edges.
Types of Telephoto Lenses
Telephoto photography can be done with any camera system that allows you to swap out lenses. This includes DSLR, mirrorless, and even some film cameras. Leading lens manufacturers like Canon, Nikon, Sony, and Sigma offer a wide variety of telephoto lenses to suit different photography needs and budgets. These lenses range in focal length from moderate zooms to super-telephoto lenses that can reach over 500mm.
Common Telephoto Lens Focal Lengths

Here are some of the most common focal lengths used in telephoto photography and their ideal applications:
24mm–70mm Lens: This lens sits in between wide-angle and telephoto, making it versatile for multiple types of photography. It’s particularly good for landscapes because it offers both wide-angle shots and the compression effect at the longer end of the focal length.

Landscape Photography
70mm–200mm Lens: This is one of the most popular zoom lens ranges for portrait photographers. It allows you to create flattering portraits while also emphasizing background elements, like mountains or skyscrapers, to make them seem larger than life.

Mountain Photography
200mm–500mm Lens: These lenses are ideal for wildlife and sports photography, as they give you the ability to shoot distant action up close. A 500mm lens, for example, is often used by photographers capturing wildlife in remote areas.

Wildlife Photography
300mm and Beyond: Lenses with focal lengths of 300mm or more are classified as super telephoto lenses. These offer maximum magnification and are commonly used for bird photography, wildlife photography, and any situation requiring extreme zoom.

Wildlife Photography with Extreme Zoom
Zoom Lenses vs. Prime Lenses
When choosing a telephoto lens, you’ll often face a decision between zoom lenses and prime lenses. Both have their advantages and drawbacks.
Zoom Lenses
Telephoto zoom lenses allow you to adjust the focal length within a given range (e.g., 70mm to 200mm). This versatility makes them an excellent choice for photographers who need to react quickly to changing subjects or want to cover a broad range of situations. However, zoom lenses often sacrifice some image sharpness, particularly at their extreme focal lengths.
Prime Lenses
A prime telephoto lens has a fixed focal length, meaning you can’t zoom in or out. The major benefit of using a prime lens is that it typically provides better image quality—sharper images, wider apertures (for more light), and less distortion. However, the limitation is that you need to physically move to change your composition.
For example, a 500mm prime lens is highly favored by bird photographers who need maximum clarity and a wide aperture to capture fast-moving birds.
The Impact of Crop Factors
Before purchasing a telephoto lens, it’s important to know your camera’s sensor size—whether it’s a full-frame or crop-sensor camera.
- Full-Frame Cameras: These cameras use a larger sensor that captures the entire image as you see it. If you use a 200mm telephoto lens on a full-frame camera, it will give you exactly 200mm of magnification.
- Crop-Sensor Cameras: These cameras have smaller sensors that “crop” the image slightly. This effectively makes your lens feel like it has a longer focal length. For example, a 1.5x crop factor means that a 200mm lens will behave like a 300mm lens on an APS-C camera.
Knowing your crop factor is crucial when selecting the right lens for your needs, especially if you’re working with a camera that isn’t full-frame.
Popular Subjects for Telephoto Photography
While telephoto lenses can be used for nearly any subject, there are certain genres where they truly shine.
1. Wildlife Photography
Telephoto lenses are a must for wildlife photographers. Whether you’re photographing birds in flight or big game in the wild, these lenses let you get up close without disturbing the animals. A 400mm or 500mm lens is often the minimum for wildlife shots, giving you the necessary reach to capture details from a safe distance.
2. Portrait Photography
Telephoto lenses are fantastic for portraits, especially in the 70mm to 85mm range. They allow for flattering facial features and create a pleasing background blur (bokeh). The compression effect is also helpful in portraits, as it reduces the distortion you might see with wide-angle lenses.
3. Landscapes and Skylines
A telephoto lens can make distant landscapes, like mountain ranges or city skylines, look larger and more impressive. By compressing the scene, telephoto lenses make objects in the background appear closer to the foreground, adding depth and interest to your landscape shots.
Best Practices for Telephoto Photography
Using telephoto lenses can present some unique challenges. Here are some tips to help you get the most out of your gear:
1. Use a Tripod (Telephoto Photography: The Ultimate Guide)
Telephoto lenses are heavier than standard lenses, which makes them prone to camera shake. A sturdy tripod is essential to keep your camera still. For even greater stability, use a monopod or gimbal when shooting with the longest lenses.

2. Increase Shutter Speed (Telephoto Photography: The Ultimate Guide)
If you’re not using a tripod, a higher shutter speed can help eliminate motion blur caused by camera shake. A common rule of thumb is to set your shutter speed to the reciprocal of your focal length. For example, with a 400mm lens, aim for a shutter speed of 1/400 second.
3. Enable Image Stabilization (IS) (Telephoto Photography: The Ultimate Guide)
If your lens has IS (also known as vibration reduction), make sure it’s activated to reduce the effects of camera shake, especially when handholding your telephoto lens.
4. Use a Remote Trigger (Telephoto Photography: The Ultimate Guide)
To prevent shake from pressing the shutter button, consider using a remote shutter release or a camera timer. This can make a big difference, especially at long focal lengths.

Editing Telephoto Photos
Telephoto images often require some post-processing to make them look their best.
- Eliminate Blurry Shots: The first step in editing is to cull any blurry or out-of-focus images. Telephoto shots are especially prone to blur from camera shake, so it’s important to weed out those images early.
- Dehaze: When shooting distant subjects, especially in foggy or hazy conditions, use Lightroom’s Dehaze tool to improve clarity and contrast.
- Sharpen and Adjust Colors: Once you’ve eliminated the blurry images, sharpen the focus and fine-tune the colors. Telephoto shots sometimes benefit from extra contrast and saturation adjustments to make distant elements pop.
Conclusion
Telephoto photography opens up a world of possibilities, allowing you to capture distant subjects in stunning detail and clarity. Whether you’re photographing wildlife, portraits, or landscapes, the long focal length and compression effect of telephoto lenses give you the ability to create dramatic and captivating images. While the gear and techniques may take time to master, the results are well worth the effort.
Remember, the best way to learn telephoto photography is to experiment. Get out there, try different lenses, and explore different subjects. Soon enough, you’ll discover how telephoto photography can help you capture the world in new and exciting ways.

